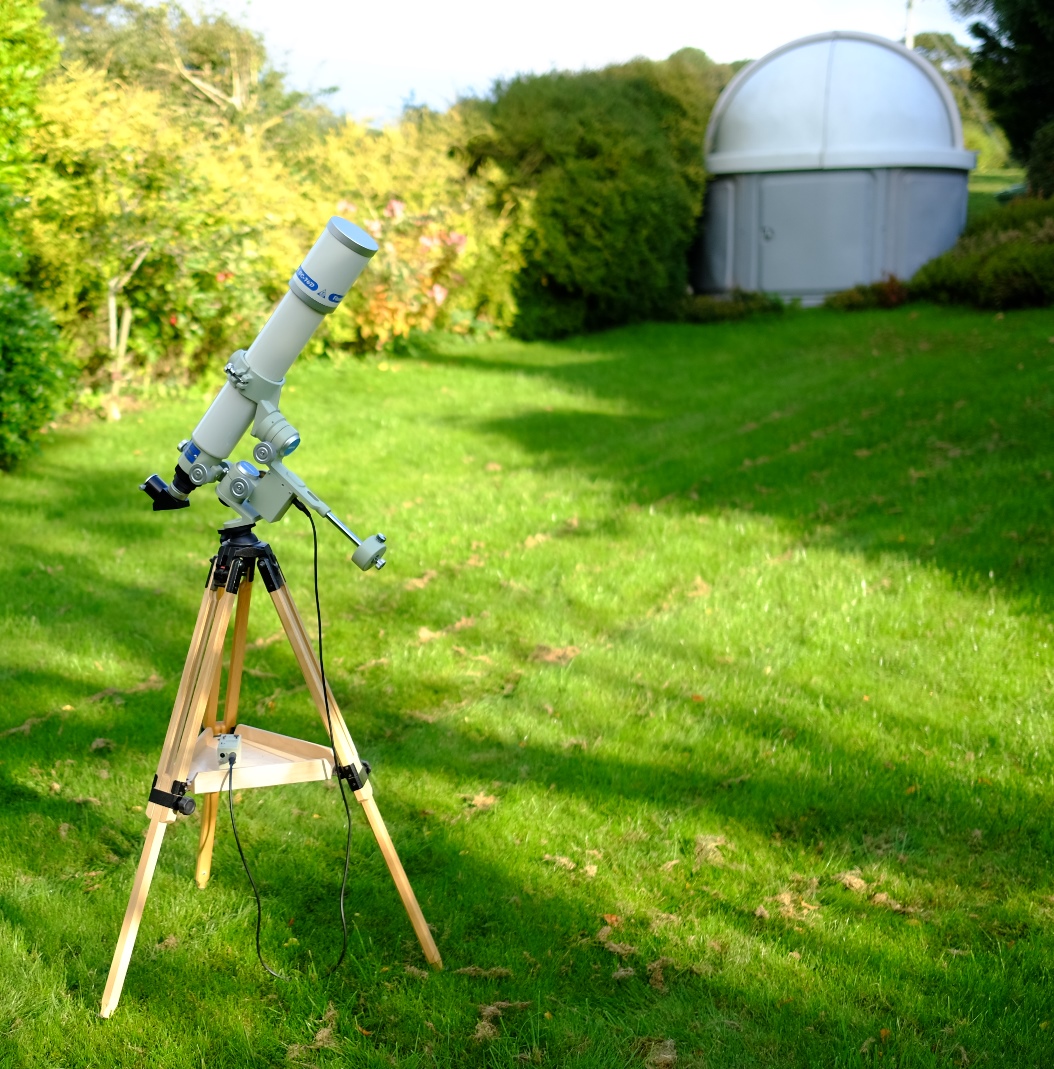
Takahashi
FC-76DC / FC-76DCU Review

When Takahashi discontinued the FS series, they replaced the
four-inch FS-102 model with an updated version of the older FC-100, with no nasty
heavy metals in the flint and optimised for imaging. Then a few years later,
they did the same with the three-inch version, replacing the old FS-78 with two
new FC-76D models.
The FS series refractors were F8 fluorite doublets of
Fraunhofer design (fluorite at the front) in oversized tubes. They were aimed
squarely at the solar system observer, with old-style film imaging as a
sideline. In contrast, the new FC-76D models are Steinheil fluorite doublets
(fluorite at the back) in slim, lightweight tubes with a slightly faster F
ratio of 7.5 and designed with the digital imager in mind (though still great
for visual).
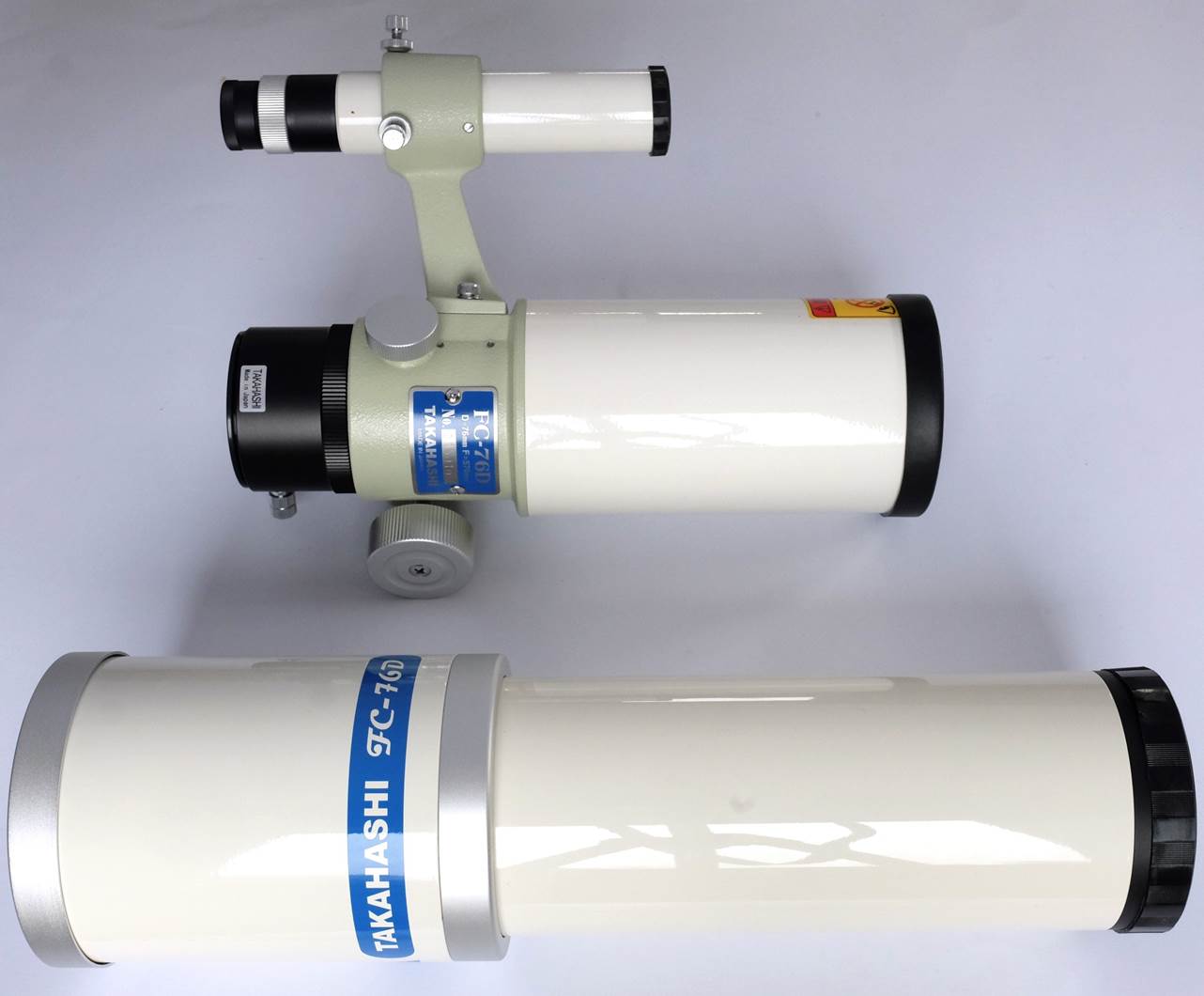
The FC-76D comes in two variants: the FC-76DC and FC-76DS. The
FC-76DC on review here is the lighter and cheaper of the two variants, more
suited to visual use, whilst the FC-76DS is oriented towards the imager. The original
FC-76DC had a standard tube, but the current version (the FC-76DCU) screws in
half for easy transport.
Note: in this review I refer to the
‘FC-76D’ when discussing optical performance common to both models,
‘FC-76DC or DCU’ when discussing specifics of that tube.
At
A Glance
|
Telescope |
FC-76DCU |
|
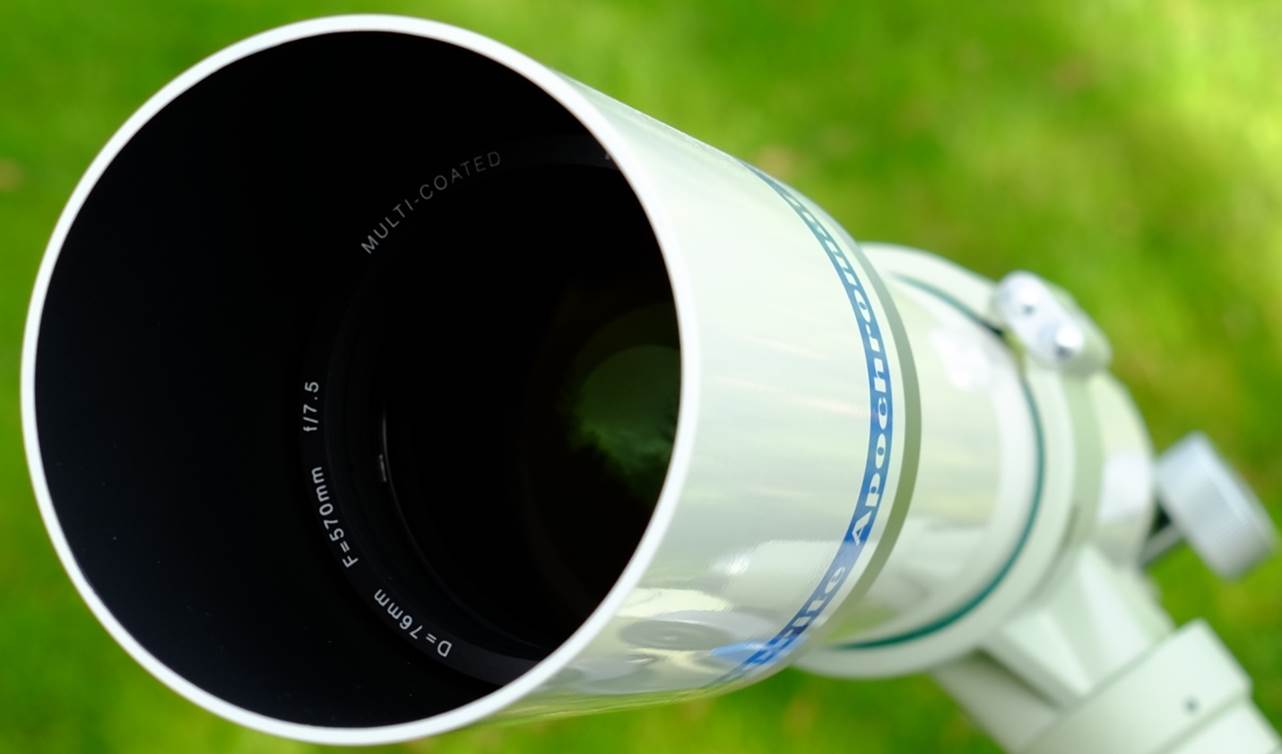
Aperture |
76 mm |
|
Focal Length |
570 mm |
|
Focal Ratio |
7.5 |
|
Length |
329 mm + 335 mm |
|
Weight |
1.8 Kg OTA/ ~2.4 Kg incl. ring, finder |
What’s
in the Box?
I don’t usually photo telescope
unboxings – just a big brown cardboard box after all. But
Takahashi’s cartons are unlike any I’ve seen: The FC-76DCU came
triple boxed, each Russian-doll layer cleverly separated by fold out spacers
– box origami!


Design
and Build
The FC-76DC on review here has a fixed dew-shield in a split
80mm tube and with the small 2” focuser from the FS-60C.
The imaging-oriented FC-76DS version has a sliding
dew-shield, a larger (2.7”) focuser to handle bigger cameras and a 95mm
tube like the old FS-78; but it’s much heavier than the FC-76DC and more expensive
too. Optics are the same.
A new imaging-oriented version for 2024 is the FC-76DP. This
takes the back end of a modern FC-100DF/DZ with a section of 95mm tube and
grafts it onto the front end of an FC-76 DCU. It looks weird, but this allows
for a wider focuser tube to avoid vignetting large sensors and the adoption of
a new reducer that speeds the optics dramatically to F4.8/365mm.
This newer FC-76DCU version is
identical to the original FC-76DC in every way, except that it screws in half.
This is a great idea because the FC-76DC is lightweight and slim, but quite
long and wouldn’t fit in carry-on luggage. Putting a thread in the middle
reminds me of those adventure-touring bike frames you can get in two halves
with connectors – a simple idea that makes a big difference to practical
transport. The two halves of the FC-76DCU would fit in my wife’s designer
handbag.


Optics
Like other
Takahashi doublet objectives, the FC-76 has a crown element made of the mineral
fluorite to give the best possible correction for false colour fringing. You
can see this for yourself, because a laser scatters in glass, but vanishes in
fluorite.
The new FC-76D
models have all reverted to a Steinheil configuration for their air-spaced
doublet that puts the fluorite element at the back, like the original FC-76,
helping protect it (fluorite is quite fragile). Their forerunner, the FS-78,
had a conventional Fraunhofer design that put the mineral up front. Unlike the
older FC-76, though, all optical surfaces in the modern Steinheil lens are
fully coated.
Another
departure from previous Takahashi 3” doublets is a reduction of focal
ratio to F7.5 from F8, giving a focal length of 570mm. Half an F-number may not
sound a lot, but makes quite a difference to exposure times for imagers. The
‘D’ in the name indicated the optic has been optimised for imagers
in other areas too, with excellent coverage and low field curvature/coma off
axis. In addition, the spot sizes of the original FC-76 have been reduced and
the optic pulls the violet G-line closer into the main crossing to reduce
violet blur in images.
Like other
Takahashi objectives, this one was made by Canon/Optron in Japan. It’s in
a proper little cell and has superb coatings, but the cell screws onto the tube
and doesn’t have collimation screws like its forerunner the FS-78 did.
Another optimisation for imaging is to keep the foil spacers out of the light
path for improved stellar images.
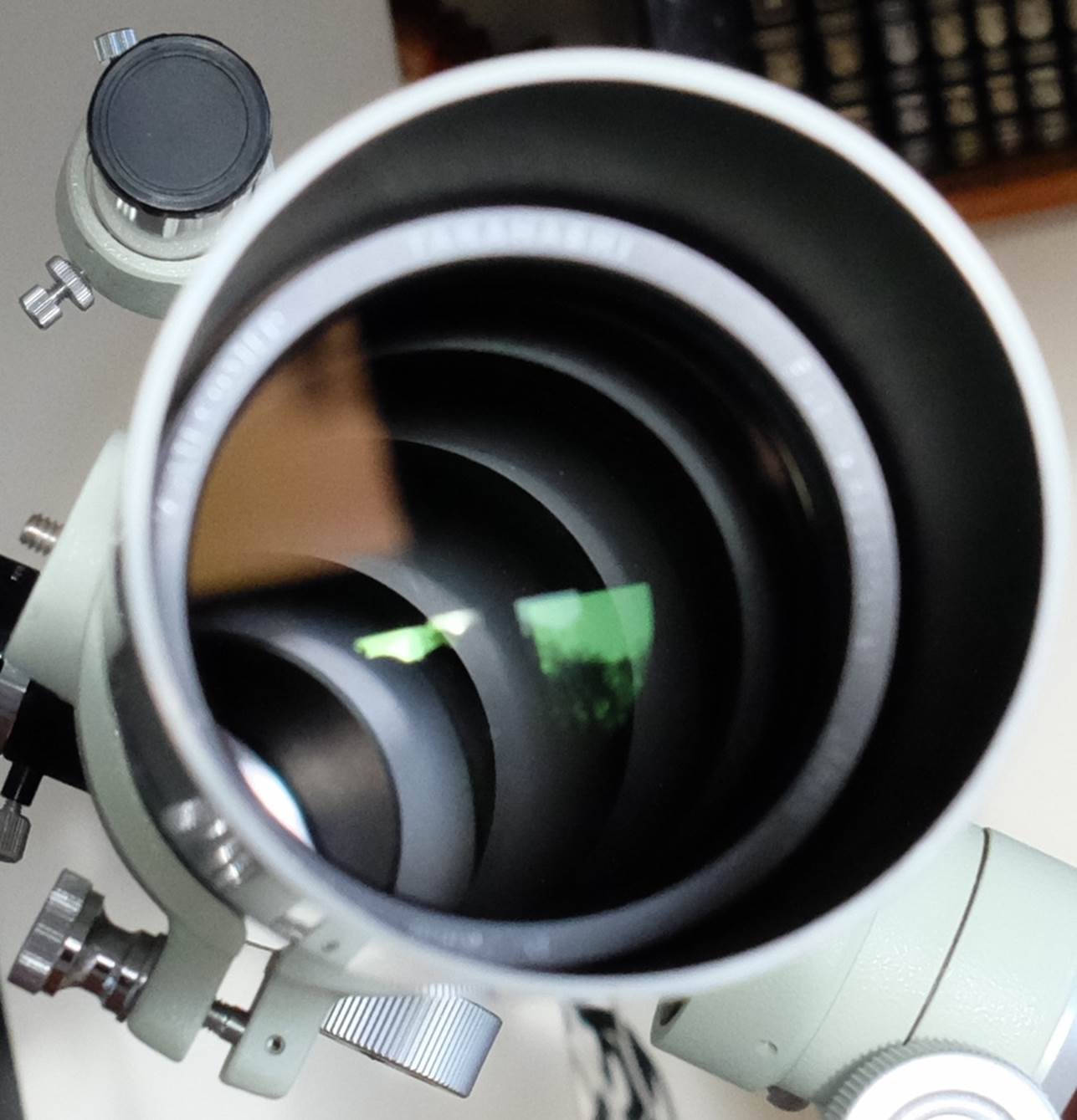

Canon
fluorite doublet has some of the best coatings you’ll find anywhere. Tube
has classic knife-edge baffles, despite compact dimensions.
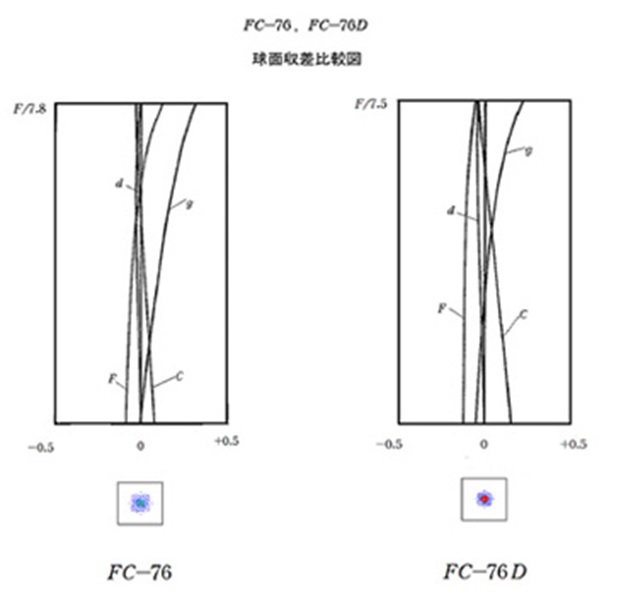
D for Digital
– the new FC-76D improves on
spot sizes and violet blur compared to the original.
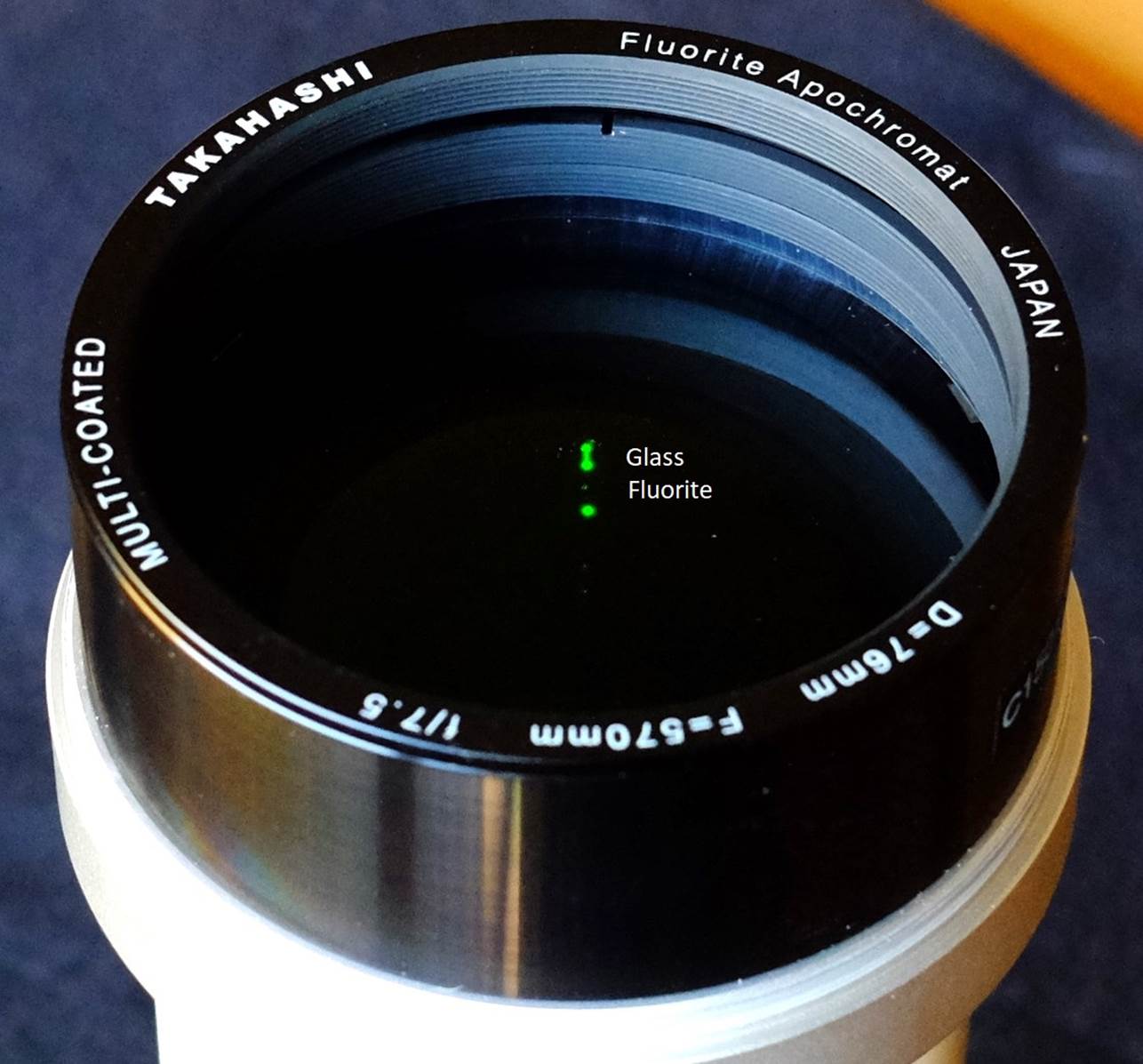

Laser
confirms that it’s a Steinheil doublet with the fluorite at the back.
Tube
The 80mm
diameter tube splits along a central thread - the focuser section is 329mm
long, the objective 335
mm. The thread seems robust and well-machined, but I would advise mating it
with the tube held vertically to reduce the possibility of cross-threading.
With a thread-on (i.e. fixed)
dew-shield and a thin tin dew cap (gone is the old FS-series ‘manhole
cover’), it weighs just 1.8 Kg for the bare OTA and around 2.4 Kg
including the ring and finder – remarkably light for a 3” APO and
much lighter than the either the FS-78 or the FC-76DS, which both weigh in at over
3 Kg.
Despite being so slim-line, the tube still manages to fit in
four knife-edge baffles to control stray light, carefully blacked with matte
paint.
The finish is standard Takahashi
– a beautifully enamelled off-white tube with love-it-or-loathe-it
lime-green (or lately blue) for the focuser and silver detailing where the FS
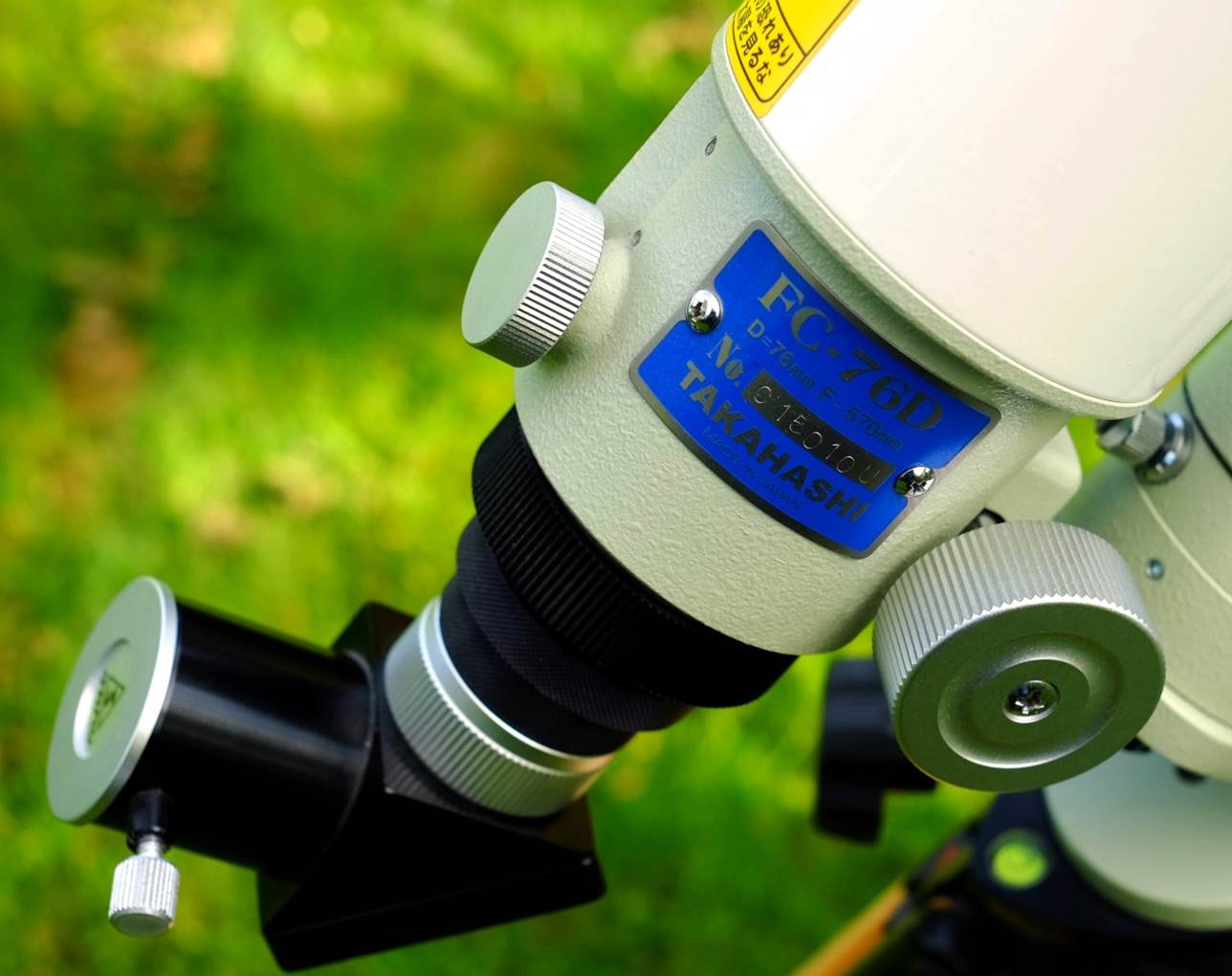
series had blue enamel. Each one has an individual serial number plate on the
focuser as always.
Focuser
The 2”
drawtube FS-60 focuser is a proven unit. There is no micro-focuser as standard,
but Takahashi focusers are some of the smoothest around and have a unique feel
that I love. This one has the old solid metal knobs, but newly bought examples
may have hollow plastic knobs that look the much the same.
The focuser
is equipped with a large lock-knob on top that is wonderfully progressive and
free of image shift; it has the standard mounting holes for a Tak’ finder
bracket.
The back of the
focuser has an M50 thread and can be fitted with 1.25” or 2” visual
backs and various other accessories.
The main
downside with this very short focuser can be image shift, but I have come to
suspect this mainly happens on units with the shims worn by lots of use with
heavy CCD cameras. This (new) example is fine and is quite robust enough for a
heavy DSLR like a Canon EOS5D, but it might struggle with massive cameras or binoviewers.
The other
downside is limited travel, which means extension tubes are often needed for
long focus eyepieces or for imaging. After-market focusers are available, such
as the superb Feathertouch (see below).
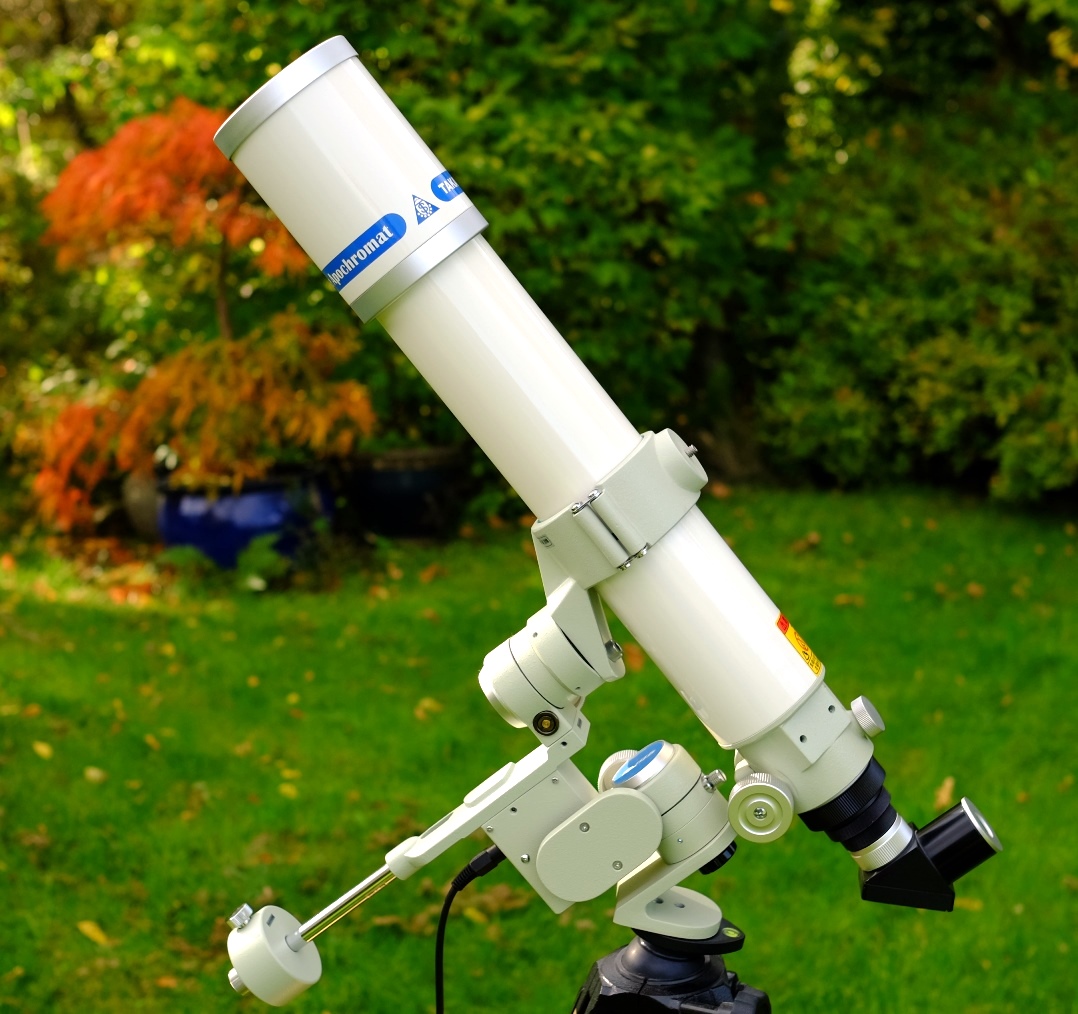


Takahashi’s tiny Teegul SP2 mount
easily holds the FC-76.
Mounting
This is an
area where the FC-76D really improves on the old model (and the FS-78 too),
which were big and fairly heavy and needed an EQ5 sized mount. The FC-76D OTA
is so light and compact that any mount will take it, including
Takahashi’s own tiny Teegul mount, which is surprisingly stable and vibe
free with the FC-76DC on a light Berlebach tripod.
The
FC-76D/Teegul combination makes for a powerful and portable system to rival
Questar and would be great for eclipse chasers.
Accessories
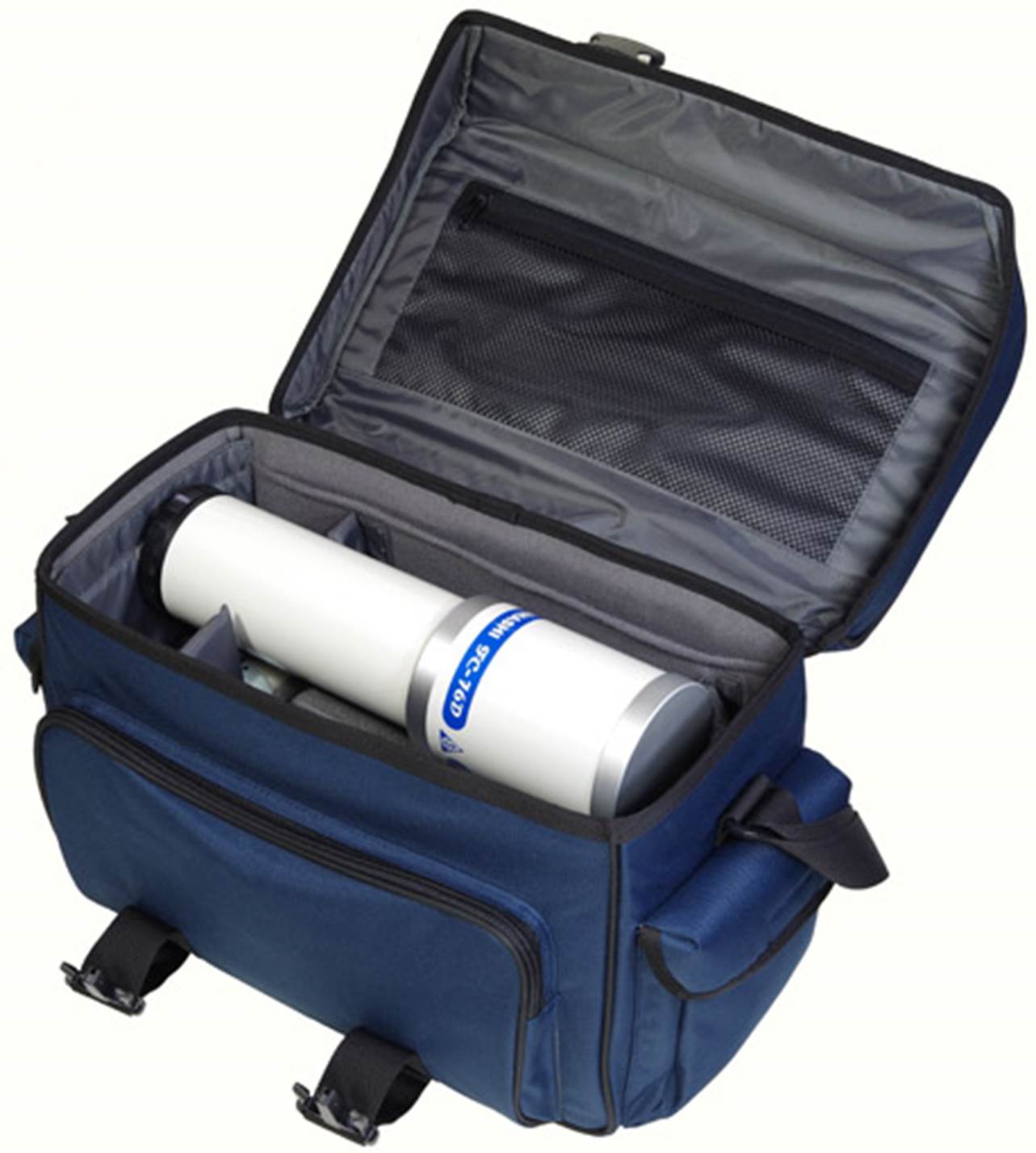
The first
fifty FC-76DCUs were sold with a rather fetching blue camera bag that just fits
both parts of the split OTA. A similar bag is still available as an accessory
in some markets.
Numerous
other accessories are available, including a rotator for the focuser, various
extensions and adapters and two flattener options:
The FC-76 shares its reducer with the
FC-100D. It speeds up the FC-76D to 417mm (F5.5), but the image circle of 36mm
isn’t great for larger sensors.
Alternatively, Tak’ can supply an
adapter ring for their inexpensive 1.04x multi-flattener. It extends the focal
length slightly to 594mm (F7.8), but gives you a flat image circle of 40mm that
should provide decent coverage on a full-frame sensor.
To extend the focal length, the split
tube FC-76DCU also has another accessorized trick up its sleeve, buried in the
user manual – slot in the CQ 1.7x extender module for the FS-60Q and you
have the best planetary and Lunar 3” APO I have ever seen. But since the
FC-76Q briefly became a product in its own right, I’ve reviewed it
separately here.
Finally, the lack of focus travel could
be addressed with aftermarket focusers from Moonlite or Starlight Instruments
(see pic below); a 1.5”-2.5” long drawtube would probably be ideal,
but check with the vendor. The Moonlite focuser can be fitted with a
Takahashi-standard finder base too.


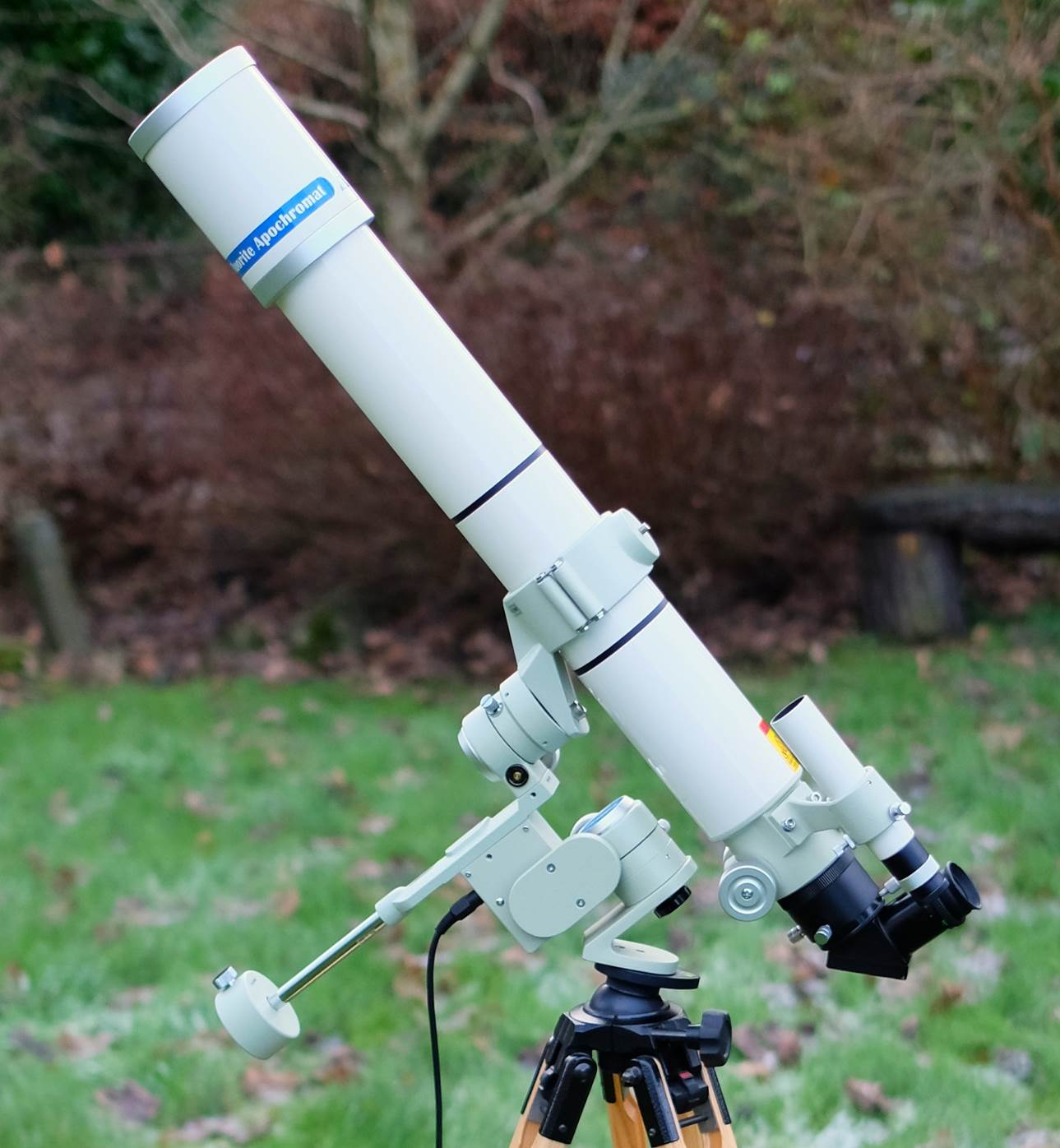
FC-76DC fitted with an after-market Feathertouch focuser.

With the ‘Q’ module
extender, the FC-76DC becomes the FC-76Q – an F12.6 planetary/lunar
specialist with a very flat field.
In
Use – Daytime
The daytime field of view is flat and
sharp and mostly false colour free, but this is largely academic because the
FC-76DC is too probably large to mount on a photo tripod and use as a spotter
(unlike say a Borg 71FL).
In
Use – Astrophotography
Off-axis aberrations are very modest
for a doublet and coverage excellent – even on full frame. Violet bloat
on bright O-A stars is well controlled. See image of M42 below (as usual, a
single frame, unprocessed apart from a reduction in size).
You can really tell Takahashi designed
the FC-76D for digital imaging (hence the ‘D’). For APS-C sensors
you could get away without a flattener to get you started, a big advantage over
most F6 doublets where a flattener is essential. Coverage is good and curvature
well controlled, even at full-frame – see corner crop below.
The main real drawback of the FC-76DC
for imaging is focus travel: you might need to be creative with extensions
and/or judicious positioning of the camera nosepiece.
Imaging the Moon can tell you a lot
about how a scope performs in terms of sharpness, resolution and contrast at
high image scale and how it handles seeing, revealing flaws you miss visually.
I managed to image the Moon with FC-76D at exactly the same phase and under
similar seeing conditions to the FS-78 years back. Zoomed right in, the images
are very similar, suggesting the FC-76D gives little away to the older scope in
these areas.
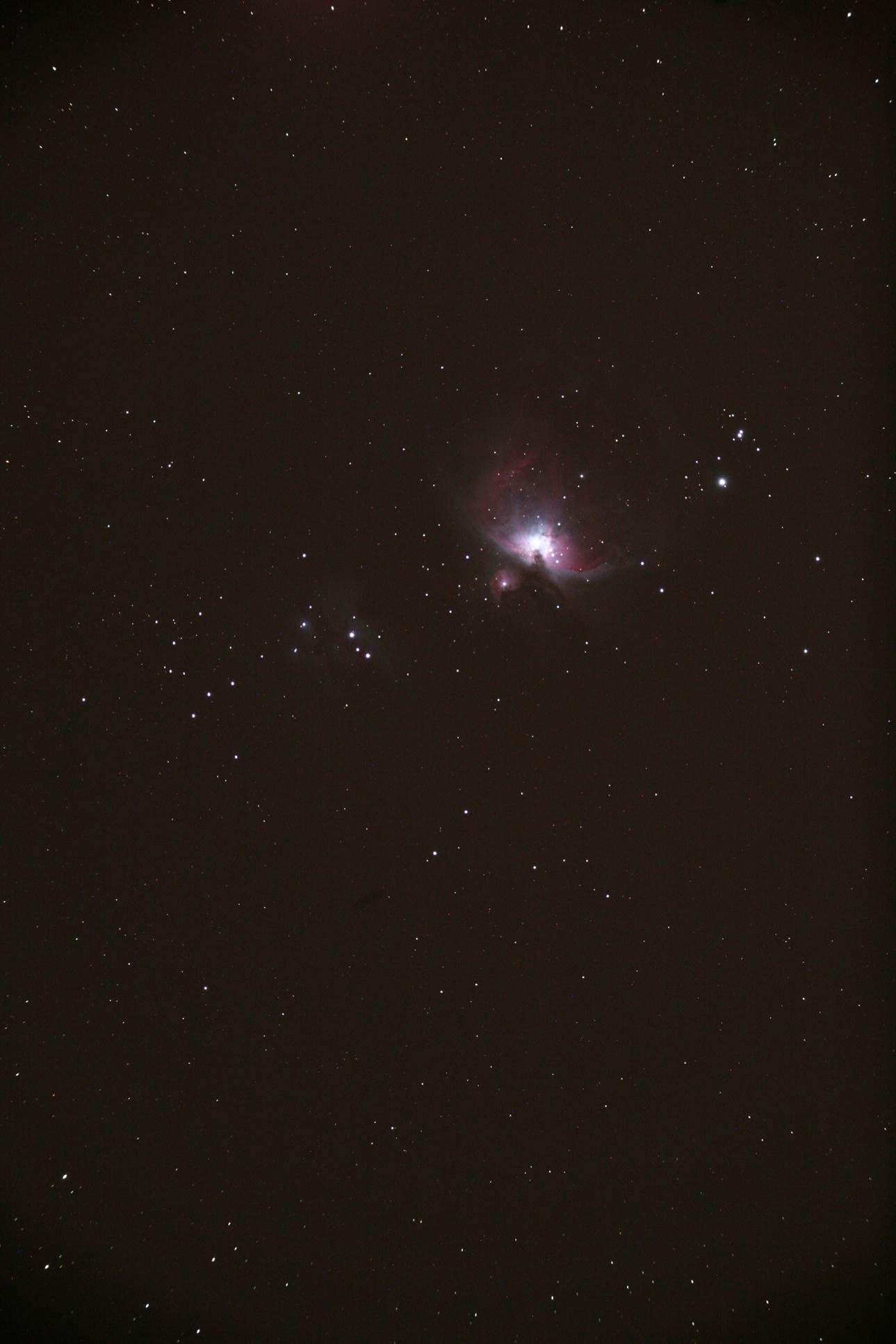

Full-frame image of M42 with FC-76D and
Canon EOS 5D – 45s at ISO 1600.
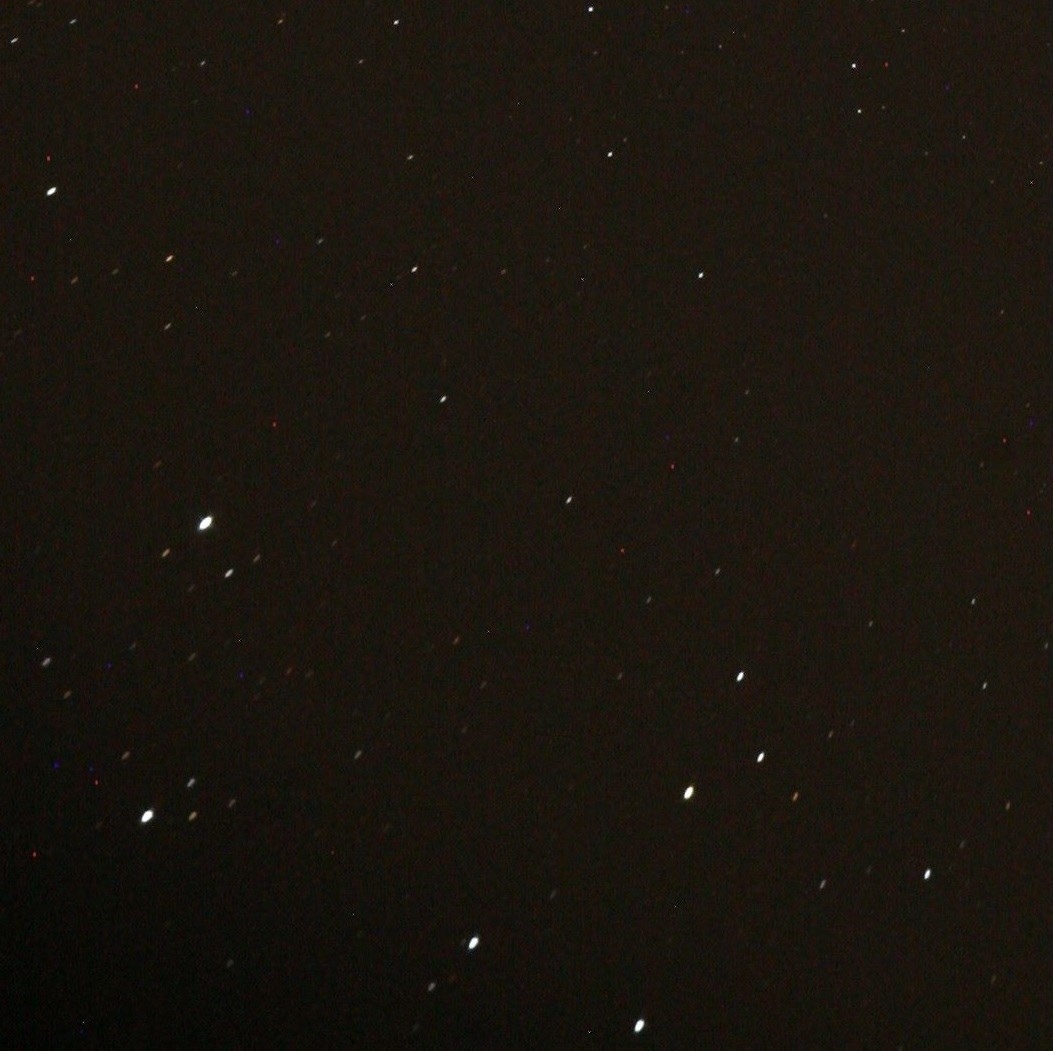

Bottom left corner cropped from
full-frame image above.
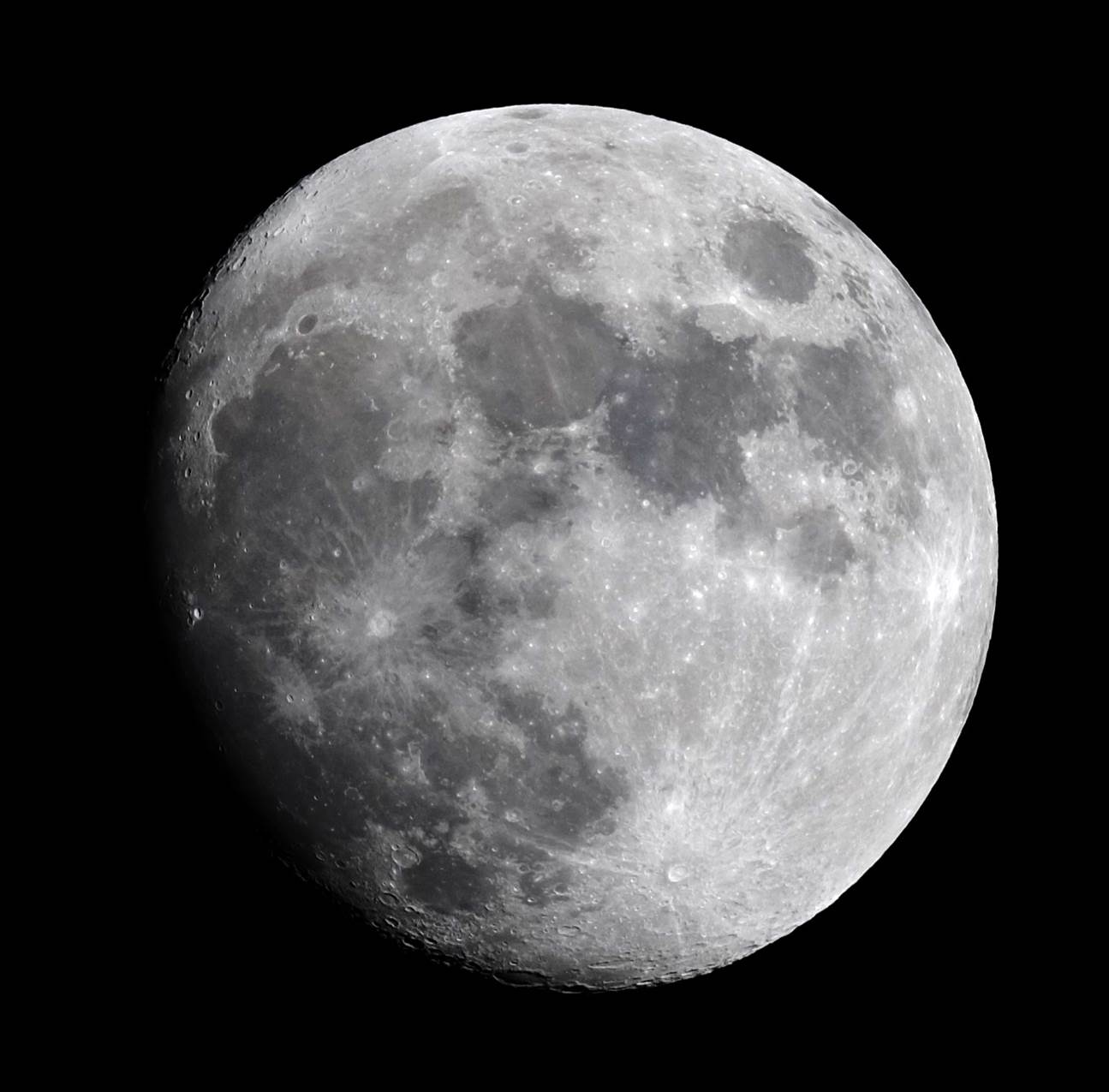

Moon at prime focus with FC-76D.
In
Use – The Night Sky
General
Observing Notes
Cooldown is
benign and rapid – a godsend if you are used to waiting for triplets,
Maks or SCTs (and waiting … and waiting …).
Despite the
longish f-ratio, perfect focus is such an absolute point that finding it would
be easier with a microfocuser; as it is you need to
be practised to nudge in perfect focus with the tiniest movement of one of
those silver Tak’ wheels.
As usual, the
little Tak’ delivers hard, very white, very contrasty views. There is
minimal stray light around Venus or the Lunar limb, no nasty halos around
Jupiter or red blur around Mars. This really is what you are paying for
compared to a cheaper optic of modest quality.
The FC-76D in
standard form isn’t great for binoviewing
– there just isn’t enough in focus travel and many Eps won’t
come to focus even with the refractor OCS in the nosepiece of my Denk’
Standards.
Star
Test
The star test
is all but perfect – very similar either side of focus. Even more
impressive is the perfect, faint, in-focus diffraction ring around a bright
star on a steady night at 163x.
The
Moon
Takahashis of
old have always been great Lunar scopes and the FC-76D is no exception: it gives
one of the best views of the Moon I have had with a 3” refractor. With a
5mm Type 6 Nagler giving 114x, the whole Moon fits in the field and it is sharp
and full of detail and contrast from limb to limb.
On a
13-day-old gibbous Moon, in steady seeing at 163x with a 3.5mm Nagler, I can
explore a wealth of terminator detail: several bright craterlets on
Plato’s dark floor; the strange and solitary black shadow from
Promontorium Laplace; the Gruithuisen domes; stripes in the crater wall of
Aristarchus; hints of rilles in Gassendi.
Venus
Venus showed
a brilliant white crescent with no flare or stray light and virtually free of
false colour (just a hint of gold out of focus), even at 143x with the Nagler
zoom set on 4mm. This is where the longer focal length of the FC-76D shows
– Borg’s F5.6 90FL shows quite a lot of proper purple-and-green
false colour on Venus at the same magnification.
Mars
At just 5.7”
in size, Mars was very sharp with no false colour at up to 190x with a 2-4mm
Nagler zoom. I spotted hints of albedo markings on its minute ochre disk. Small
F6 APOs often fail on Mars, giving a mushy soft view because their Strehl is
poor in the red; not so the FC-76D.
Jupiter
At 143x with a 4mm Nagler zoom, Jupiter
showed a crisply-defined cream disk free of false colour or softness, with
quite a lot finer detail – narrow belts north and south of the main NEB
and SEB, shading in the polar hood and hints of dark storms.
Deep
Sky
I don’t
usually use small scopes much now for deep sky, preferring to use big-eye binos for quick DSO sessions. But I thought I should try it
out for this review and ended up having a lot of fun. For most of the easier
stuff, I just swept using a 32mm Plossl and then
upped the power with a 15m Panoptic as required; I never needed the finder.
Orion’s
Great Nebula looked wonderful, with lots of nebulosity sweeping into space.
Bode’s twin galaxies were much more interesting and distinctive than they
have a right to be through such a small aperture. The Pleiades were classic
diamonds-on-velvet embedded in faint wisps of nebulosity. The Starfish and
Pinwheel Clusters showed their sweeping arms of stars and looked great. The
Crab Nebula was easy to spot north of Zeta Tauri and its shape was readily
discerned. The Andromeda Galaxy was bright and showed hints of dark lanes; the
wide field easily encompassed most of it.
The FC-76D
seems good at splitting doubles, too. Epsilon Lyrae was easy. On a night of
fairly steady seeing I had one of my best ever views of Rigel, with Rigel B
much more obvious than usual, perhaps due to the FC-76D’s high Strehl
objective that packs so much of the light into the Airy disk and less into the
space around it.
Surprisingly (I thought) the FC-76D proved really
good at visual deep sky – much better than any 60mm scope and better than
some larger scopes I’ve seen; blame that high-contrast, high-Strehl lens.
Summary
As with previous 3” Takahashi
fluorite doublets, the FC-76D offers quick cooldown and razor-sharp views of
everything – the Moon, planets and deep sky - with minimal false colour.
If its predecessor, the benchmark FS-78, gave a better view, it wasn’t by
much. Ditching the lead and arsenic, speeding it up and returning to a
Steinheil configuration hasn’t spoiled those essential Tak’
fluorite-doublet values.
Unlike the FS-78, though, the FC-76DC
is lightweight and highly portable for its aperture – especially in this
split-tube FC-76DCU version. And that half F-number extra speed is a bonus for
imagers, as is the low level of violet blur. The ‘D’ for
Digital-imaging optimisation seems to extend to flatness and coverage too
– both pretty decent even without a flattener.
The only real negative point is the
focuser – perfectly smooth and accurate and largely free of image shift,
it could just do with another few cm of travel. I can see quite a few FC-76s
ending up with Feathertouch or Moonlite focusers.
No, the FC-76DC is not cheap, but
current prices are competitive with other small APOs in the premium class
(including Borg’s, which also use Optron fluorite objectives). Build
quality is usual Tak’ – simple but superb.
The FC-76DC is something of a sweet
spot in the range: substantially lighter and cheaper than an FC-100, it offers
much better all-round performance even than an FS-60Q.
If you need a really portable small APO
that will do both imaging and high powers for the Moon and planets, one that
cools fast too, you just found it – highly recommended.
